The Transactional Net Margin Method (TNMM) is the most popular method for determining transfer pricing in Vietnam and around the world. The TNMM method is based on comparing the net profit margin of an enterprise with independent companies performing equivalent functions, thereby proving that internal transactions comply with the market principles according to Decree 132/2020/ND-CP. To learn more about valuation methods Related Transactions (Transfer Pricing) other, you can refer to at This.
This article fully analyzes the principles, implementation process and important notes when applying the comparative profit method to help businesses build a solid and effective pricing profile.
Overview of the comparative earnings method (TNMM)

Core concepts and principles
The Comparable Profits Method (TNMM) works on the principle of comparing the net profit earned by an associated party from internal transactions with the net profit of independent parties performing equivalent activities.
The core principle is: The net operating profit of the related party under analysis (Tested Party) must be within the range of profit that an independent company would achieve when performing the same functions, taking the same risks and using the same assets.
The application of the TNMM method is an important compliance requirement, recognized by law and detailed in Decree 132/2020/ND-CP of the Government of Vietnam.
Outstanding advantages of TNMM
The Comparative Profit Margin Method (TNMM) is preferred over traditional methods (such as CUP or CPM) due to its flexibility and practicality in complex business environments.
Outstanding advantages include:
- Reduced Sensitivity: The TNMM method is less sensitive to small differences in functions, assets, or risks between the Analyzed Party and independent companies. Small differences in contract terms will have less impact on the Net Profit Margin (NPI) than on Price or Gross Profit Margin.
- Easy to find data: Net profit data is often publicly available in the financial statements of independent companies, making finding comparable data more feasible.
- High flexibility: The Comparable Profits method can be applied to many complex types of related-party transactions, including integrated supply chains or internal service contracts.
6-step process to apply TNMM
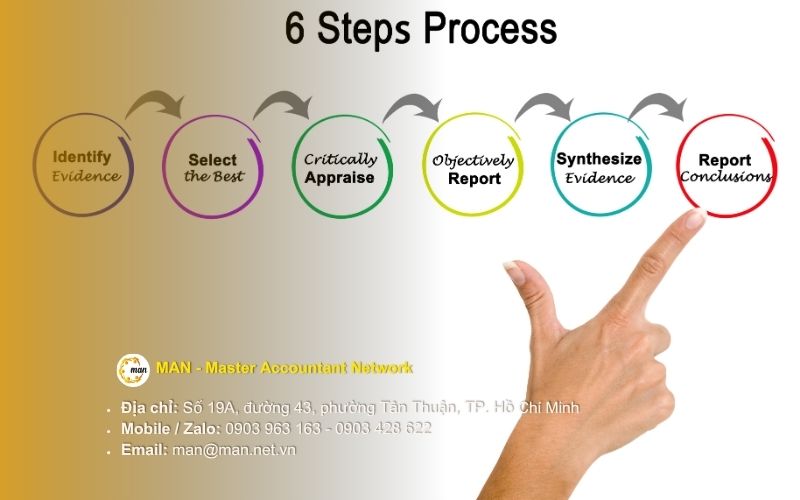
To apply the Comparable Earnings Method correctly and compliantly, a business needs to follow a systematic six-step process:
Step 1: Analyze functions, assets and risks
This is the foundation of any TNMM analysis of related party transactions. This step aims to accurately determine the economic role of each party in the transaction (manufacturer, distributor, service provider, etc.).
The following factors should be listed and carefully evaluated:
- Function: Main activities performed (purchasing, marketing, R&D, production, logistics).
- Assets: The assets used (tangible assets, intangible assets such as brands, technology).
- Risks: The significant business risks that the party is exposed to (inventory risk, credit risk, market risk, warranty risk).
Step 2: Select the side to be analyzed
Choosing the Tested Party is the decisive step for the success of a comparative study.
As a rule, a company should always choose the related party that performs the simplest function and has the least unique intangible assets or the greatest risk. Choosing the right Tested Party is the key to optimizing the results of applying the Comparative Profits Method.
Step 3: Select net profit margin (NPI)
The net profit margin (NPI) chosen should reflect a reasonable relationship between profit and the functions and assets used by the party.
To have a visual view of the suitability of the indicators, we refer to the following table:
| Net Profit Margin (NPI) | Calculation formula | The most suitable type of business/transaction |
|---|---|---|
| ROS (Return on Sales) | Net operating profit / Revenue | Popular for distributors, sales with inventory and market risk. |
| RPT / COS (Return on Total Cost / Operating Expenses) | Net operating profit / Total operating expenses | Best suited for contract manufacturers, providing in-house services (cost is a driver of profit). |
| ROA (Return on Assets) | Net operating profit / Total assets | Often used for parties that use many fixed assets or large assets (Asset-intensive companies). |
Note after table: The choice of NPI must be clearly explained in the valuation dossier, demonstrating that this is the most optimal indicator to measure Tested Party's profit using the TNMM method.
Step 4: Conduct comparative research
This step involves searching for suitable Comparable Companies in financial databases.
The TNMM method of independent comparison research requires a combination of search strategies and the application of strict exclusion criteria:
- Search Strategy: Identify industry codes (e.g., NACE or SIC codes), geographic areas, and financial size limits.
- Exclusion criteria: Filter out inappropriate companies, such as those that are in the process of bankruptcy, those with significant related party transactions, or those with very different business functions.
Step 5: Determine the independent trading standard range
Once the list of suitable independent companies is available, the calculation of the Independent Transaction Benchmark using the Comparable Profits Method is carried out.
Before calculating, the required accounting adjustments must be made:
- Working Capital Adjustment: This adjustment is intended to eliminate the difference in financial risk due to the difference in days receivable, days payable and days inventory between the Analyzed Party and independent companies.
- Multi-year data: It is necessary to use net profit (adjusted) data of the comparable for 3 consecutive years to eliminate the impact of short-term business cycles.
After adjustment, we use the Quartile statistical method (from 25th percentile to 75th percentile) to determine the standard range.
Step 6: Adjust the transfer price (if necessary)
This step makes final adjustments if necessary:
- Adjustment Principle: If your company's Net Profit Margin is outside the Independent Transaction Benchmark, you must make a transfer pricing adjustment to comply. The adjustment principle in related party transactions under the TNMM method is very strict.
- Adjustment level (According to Decree 132/2020/ND-CP): According to current regulations, enterprises must adjust prices to bring the profit margin to the Median level of the standard range.
Limitations and notes when applying TNMM

Limit
Although the Comparable Profits Method is a powerful tool in determining transfer pricing, it still has limitations that businesses need to be aware of:
- Accuracy of functional analysis: Any errors or omissions in the analysis of functions, assets, and risks will lead to inappropriate NPI selection and misleading results.
- Data difficulties: Comparisons at the net profit level of the entire company sometimes do not fully isolate the effects of transactions unrelated to the related party transaction being analyzed.
Important Note
To ensure your affiliate transaction documentation stands up to the tax authorities, always adhere to these professional tips:
- Using Net Operating Profit: Always exclude Non-operating Income/Expenses when calculating NPI. Net profit should be “Operating Net Profit” to ensure comparability based only on core business activities.
- Multi-year data: Three consecutive years of data help tax authorities see that the analysis results are stable and not affected by temporary market fluctuations.
- Full documentation: All decisions in the 6-step TNMM process must be fully documented and explained in the Transfer Pricing documentation.
Conclude
The Comparable Profit Method (TNMM) offers high flexibility and applicability in diverse business environments. Full compliance with the process from functional analysis to adjustment to the Median level according to Decree 132 helps to solidify the related-party transaction profile and limit tax risks.
If you need in-depth assistance with performing Working Capital Adjustments or optimizing your GDLK profile, I am here to help.